| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2018-08-29 17:08:46 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2020-06-04 20:07:36 UTC |
|---|
| BMDB ID | BMDB0062613 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | DG(14:1(9Z)/18:0/0:0)[iso2] |
|---|
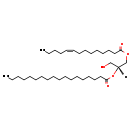
| Description | DG(14:1(9Z)/18:0/0:0), also known as diacylglycerol or DAG(14:1/18:0), belongs to the class of organic compounds known as 1,2-diacylglycerols. These are diacylglycerols containing a glycerol acylated at positions 1 and 2. Thus, DG(14:1(9Z)/18:0/0:0) is considered to be a diradylglycerol lipid molecule. DG(14:1(9Z)/18:0/0:0) is a very hydrophobic molecule, practically insoluble (in water), and relatively neutral. DG(14:1(9Z)/18:0/0:0) participates in a number of enzymatic reactions, within cattle. In particular, DG(14:1(9Z)/18:0/0:0) can be biosynthesized from PA(14:1(9Z)/18:0); which is catalyzed by the enzyme phosphatidate phosphatase. Furthermore, DG(14:1(9Z)/18:0/0:0) and alpha-linolenoyl-CoA can be converted into TG(14:1(9Z)/18:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)); which is catalyzed by the enzyme diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase. Furthermore, DG(14:1(9Z)/18:0/0:0) can be biosynthesized from PA(14:1(9Z)/18:0); which is mediated by the enzyme phosphatidate phosphatase. Furthermore, DG(14:1(9Z)/18:0/0:0) and meadoyl-CoA can be converted into TG(14:1(9Z)/18:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) through the action of the enzyme diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase. Furthermore, DG(14:1(9Z)/18:0/0:0) can be biosynthesized from PA(14:1(9Z)/18:0) through the action of the enzyme phosphatidate phosphatase. Finally, DG(14:1(9Z)/18:0/0:0) and arachidonyl-CoA can be converted into TG(14:1(9Z)/18:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)); which is mediated by the enzyme diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase. In cattle, DG(14:1(9Z)/18:0/0:0) is involved in several metabolic pathways, some of which include de novo triacylglycerol biosynthesis TG(14:1(9Z)/18:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) pathway, de novo triacylglycerol biosynthesis TG(14:1(9Z)/18:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) pathway, de novo triacylglycerol biosynthesis TG(14:1(9Z)/18:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) pathway, and de novo triacylglycerol biosynthesis TG(14:1(9Z)/18:0/22:2(13Z,16Z)) pathway. |
|---|
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C35H66O5 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 566.908 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 566.491025225 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (2R)-1-hydroxy-3-[(9Z)-tetradec-9-enoyloxy]propan-2-yl octadecanoate |
|---|
| Traditional Name | (2R)-1-hydroxy-3-[(9Z)-tetradec-9-enoyloxy]propan-2-yl octadecanoate |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | Not Available |
|---|
| SMILES | [H][C@@](CO)(COC(=O)CCCCCCC\C=C/CCCC)OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C35H66O5/c1-3-5-7-9-11-13-15-16-17-18-20-22-24-26-28-30-35(38)40-33(31-36)32-39-34(37)29-27-25-23-21-19-14-12-10-8-6-4-2/h10,12,33,36H,3-9,11,13-32H2,1-2H3/b12-10-/t33-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | PAHKOLCUPPSBEU-ALMVXPMNSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as 1,2-diacylglycerols. These are diacylglycerols containing a glycerol acylated at positions 1 and 2. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Glycerolipids |
|---|
| Sub Class | Diradylglycerols |
|---|
| Direct Parent | 1,2-diacylglycerols |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - 1,2-acyl-sn-glycerol
- Fatty acid ester
- Fatty acyl
- Dicarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid ester
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Primary alcohol
- Organooxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Alcohol
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | |
|---|
| Biofunction | Not Available |
|---|
| Application | Not Available |
|---|
| Cellular locations | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | |
|---|