| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2016-09-30 23:22:09 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2020-06-04 19:04:51 UTC |
|---|
| BMDB ID | BMDB0006461 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | - BMDB0062649
- BMDB06461
- BMDB62649
|
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Linoelaidylcarnitine |
|---|
| Description | Linoelaidyl carnitine, also known as acylcarnitine C18:2, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as acyl carnitines. These are organic compounds containing a fatty acid with the carboxylic acid attached to carnitine through an ester bond. Thus, linoelaidyl carnitine is considered to be a fatty ester lipid molecule. Linoelaidyl carnitine is a very hydrophobic molecule, practically insoluble (in water), and relatively neutral. Linoelaidyl carnitine is a potentially toxic compound. |
|---|
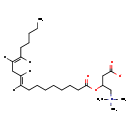
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| 3-[(9E,12E)-Octadeca-9,12-dienoyloxy]-4-(trimethylammonio)butanoate | ChEBI | | Acylcarnitine C18:2 | ChEBI | | 3-[(9E,12E)-Octadeca-9,12-dienoyloxy]-4-(trimethylammonio)butanoic acid | Generator | | C18:2 Carnitine | HMDB | | L-Linoleoylcarnitine | HMDB | | Linoelaidyl carnitine | HMDB | | Linoleoylcarnitine | HMDB | | Linoleylcarnitine | HMDB | | O-Linoelaidylcarnitine | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C25H45NO4 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 423.6291 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 423.334858933 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 3-[(9E,12E)-octadeca-9,12-dienoyloxy]-4-(trimethylazaniumyl)butanoate |
|---|
| Traditional Name | 3-[(9E,12E)-octadeca-9,12-dienoyloxy]-4-(trimethylammonio)butanoate |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | Not Available |
|---|
| SMILES | [H]\C(CCCCC)=C(\[H])C\C([H])=C(/[H])CCCCCCCC(=O)OC(CC([O-])=O)C[N+](C)(C)C |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C25H45NO4/c1-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-18-19-20-25(29)30-23(21-24(27)28)22-26(2,3)4/h9-10,12-13,23H,5-8,11,14-22H2,1-4H3/b10-9+,13-12+ |
|---|
| InChI Key | MJLXQSQYKZWZCB-OKLKQMLOSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as acyl carnitines. These are organic compounds containing a fatty acid with the carboxylic acid attached to carnitine through an ester bond. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Fatty Acyls |
|---|
| Sub Class | Fatty acid esters |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Acyl carnitines |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Acyl-carnitine
- Dicarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Tetraalkylammonium salt
- Quaternary ammonium salt
- Carboxylic acid ester
- Carboxylic acid salt
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Carboxylic acid
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organic salt
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Amine
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Status | Expected but not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | |
|---|
| Biofunction | Not Available |
|---|
| Application | Not Available |
|---|
| Cellular locations | - Cell membrane
- Cytoplasm
- Membrane
- Mitochondria
|
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | |
|---|